| February 10, 2026
Global warming potential (GWP) is a measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere over a specific time period, relative to carbon dioxide (CO₂). By definition, CO₂ has a GWP of 1, while for other gases it depends on how strongly the gas absorbs thermal radiation and how quickly that gas leaves the atmosphere, for a certain time frame considered. As gases have different atmospheric lifetimes, their GWP values depend on the time scale, in number of years, over which it is calculated. A gas which quickly leaves the atmosphere may initially have a large effect, but for longer time periods its effect becomes less important.
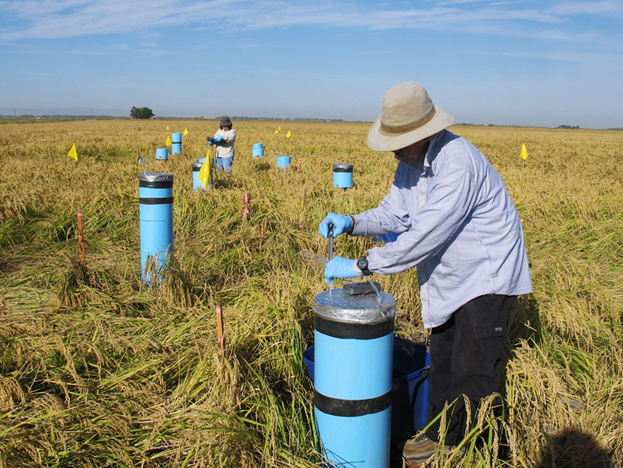
DASIG estimates combined GWP values, expressed in CO₂ equivalents using emission fluxes calculated from chamber measurements. Cumulative GWP values are calculated based on conversion factors published by the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) for 20 and 100-year horizons. Time integration for growing season or annual periods permit the determination of environmental effects and the benefits of alternative agricultural systems when compared to existing typical systems.